Role of Mental Health in Substance Use Disorder (SUD) For Log-time sobriety

Information about how mental disorder is related to substance dependence can be helpful in attaining sobriety. Sobriety must also be long-term because recovery is a concept that must be sustainable in handling addiction problems. This article is devoted to the issue of mental health in the framework of addictions and emphasizes the importance of admitting patients with Mental Health Issues as well as addictions. This includes personal and psychological health information regarding various aspects and tips. It provides vocational skills that help the intended individual to quit and stay quit for a long time sobriety.
Understanding Addiction
Alcoholism is a disease that is chronic in its nature and entails compulsive use of substances, which are seen as having undesirable consequences by the sufferer. This is due to several factors, including genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Therefore, in order for a client’s recovery to be improved, both the physical and the psychological aspects of dependency must be addressed adequately.
The role of mental health in the situation of addiction.
Some of the most common complications include depression, substance abuse, and many more related issues, it should also be pointed out that the interaction between these directions may lead to certain complications during the course of treatment therefore it may be necessary for it to interfere with both directions. This means that when addressing the issue of addiction it becomes very clear that if the condition is tackled without mentioning the issue of mental health then the results cannot be said to be very satisfactory the relapse rate is muc higher.
Kinds of Mental Illness Associated with Substance Dependence
There are several mental health disorders that often present together with addiction and stay in a cycle that is not easy to escape. These include:
Depression: This is highly associated with depression and loss of interest in day-to-day activities that can make the individual use substances to ‘treat’ their mental health.
Anxiety: Outlined as the concern and fear, which make some use substances to feel relieved from the two feelings.
Bipolar Disorder: Where persons go through oscillations of moods, for instance, bipolar disorder in which people resort to substance abuse in the course of episodes of hypo-mania and Major depressive disorder.
PTSD: Outcomes from traumatized occurrences and mainly results in substance use as a way of coping with the shocker symptoms.
All of these are critical to admit and must be treated using different therapeutic interrelations to facilitate the recovery process, showing the importance of evidence-based interventions.
The consequences of untreated psyche disease
Untreated mental health issues can significantly hinder addiction recovery, leading to various negative outcomes:
Relapse: The problem is that when people relapse, they may return to the substance as well since untreated mental health issues can complicate sobriety.
Deterioration of Physical Health: Anomalies of the mind do not spare the body and might even worsen or complicate physical health issues that are being treated.
Social Consequences: This is because untreated mental health problems affect one’s ability to have good friendships hence finding support becomes a herculean task.
It is consequently necessary to seek out the management of Mental Health Issues as a means of eradicating these negative repercussions and achieving a productive rehabilitation process.
Integrated Treatment Approaches
Having both talking sessions and the intake of substances to treat the body proves to be the best method to use to treat the patients because it will be a combination of Mental Treatment and physical treatment. There are potential ways and opportunities to combine approaches and treat diseases with the help of harmonization, such as physical activity and mindfulness. Hence, the specificity of the plan should not be questioned because the services and the needs of each person are different. By developing an individualized comprehensive treatment plan that involves the biological, sociological as well as psychological parameters of an individual, there is a massive enhancement in the recoverability of the patient.
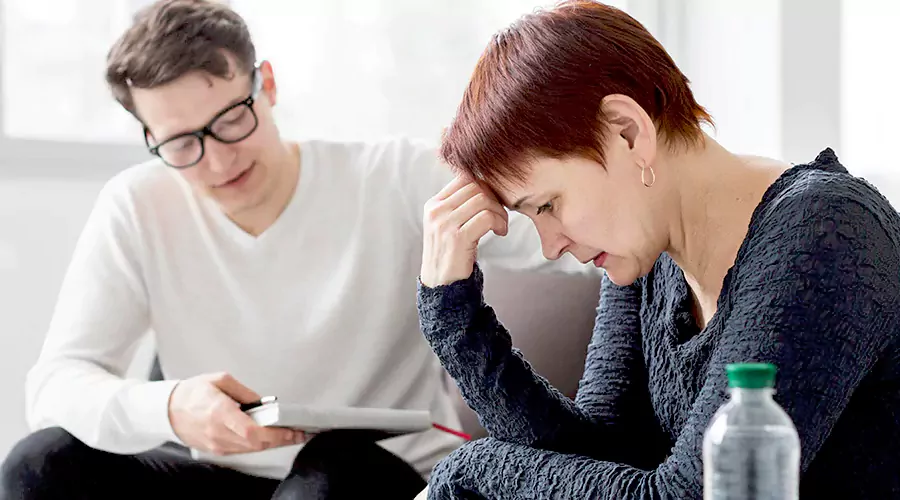

Types of Therapy Used for Mental Health Treatment in Substance Use Disorder.
These together with other therapies are used in the management of mental health in addiction recovery and give different focuses to suit the patient. These include:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): An approach that is mainly centered on the elimination of certain ways of thinking and certain behaviors that lead to substance dependence.
Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT): Focuses on affective self-regulation and interpersonal relationships improving students’ ability to regulate their emotions and their ability to deal with other people.
Motivational Interviewing: Motivates change by aiding clients to move from procrastination and/or ambivalence regarding utilizing the service towards active engagement towards recovery.
Group Therapy: Encourages participant participation and their ability to find similarities with others, which creates a group of people with the same issues.
Each of these therapies is effective in its own way, and more often than not, a blend of the therapies is applied depending on the client’s need.
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT)
Treatment which is implemented by MAT includes the prescription of drugs to control the withdrawal symptoms as well as the cravings that are associated with substance use thus enabling the patient to stay away from substances. These include Methadone, Buprenorphine and Naltrexone all of which have different mechanisms to aid in the recovery process. Nonetheless, the effectiveness of MAT has some concerns with regard to its risks and side effects of the substance being used; it is most useful when it is used hand in hand with counseling and behavior modification therapy. It also sustains a complete daily way of recovery from drug dependency in comparison to recovery merely by meeting the corporeal aspects of addiction.
Holistic and Alternative Therapies
The use of other forms of treatment enhances the conventional treatment process since it also deals with the psychological, physical, and spiritual well-being of the patients. Other practices like mindfulness Meditation, yoga, acupuncture, and art therapy will assist in leading a healthy lifestyle and enable the clients to discover more about themselves. These approaches help to release stress, and regulate emotions and feelings, which is essential for maintaining the process of a long-term recovery. Using natural and complementary treatments with the recovery plan, a patient can be covered completely and physically as well as psychologically.

Support Systems
Recovery is an important aspect that is enabled by support systems; these are people who provide emotional and tangible support. Identification of community resources, peer support, and family support are the main pillars that would ensure that someone stays sober. Especially patients or clients, need support and encouragement to come out of the stigma and depression and feel that they are normal human beings and this is possible if they have a good network of friends and relatives. Interacting with support systems is also another chance at being able to gain ideas from other people as to how they deal with recovery difficulties.
Developing Coping Mechanisms
Acquiring proper skills and learning how to react to stress in a healthy manner is very important when it comes to avoiding relapse. These include strategies for Stress Treatments including use of deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation. It is also important to live a healthy lifestyle by exercising, taking balanced diets, and making sure you get enough sleep as this will also help your state of mind. Developing coping strategies, maintaining healthy perspectives in one’s thinking and effective problem-solving skills enable the patient to effectively cope with the problems of life without resorting to alcohol.
Preventing Relapse
Relapse occurs when a recovering addict returns to use the substance and one has to avoid relapse by identifying special factors and devising an efficient relapse prevention program. External causes may be stress, public pressure, and different environmental stimuli that are linked to previous drug taking. With this knowledge of the triggers, people can learn ways how to either avoid or manage them properly. Some possible relapse prevention strategies could be weekly therapy, attendance of the meetings, and staying in touch with a sponsor. Stakeholders in the life of a person with crack addiction also need to support a patient during his or her recovery process as well as during relapse.
Self-care in Recovery
Caring for one’s self is important for the body, mind, and soul. Daily exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient rest are very basic activities that are essential for one’s health. Moreover, there are methods of improving the level of emotions, which include reading books, writing a diary, and entering the natural environment. A healthy lifestyle is another cardinal component of the treatment process as it contributes to stress- and mood regulation as well as to the development of effective coping strategies during the recovery period. Self-care is also an essential aspect in the recovery process and practicing self-care helps in asserting the value of one’s own life.

Building a Sober Lifestyle
It is highly important to develop a new sober routine that would help an individual maintain a Healthy Lifestyle and never return to substance abuse. A working concept is the creation of meaningful roles in life so that people can transform their lives and remain productive with a focus on recovery and/or sobriety. Fixed and regular schedules help create stability, and it may be useful to fill them with healthy practices and activities. Social interaction through attendance of social functions and improvement of healthy relations can also enhance the existence of sober life. Abstract By emphasizing the potential of personality changes and the attunement of a proper meaning in the life of a client, one can construct a life that tends to sustain recovery.
Addressing Stigma
Stigma surrounding addiction and mental health can be a significant barrier to recovery. Overcoming shame, educating society, and advocating for policy changes are essential steps toward reducing stigma and supporting those in recovery. Addressing stigma involves challenging misconceptions, promoting understanding, and highlighting the importance of compassionate, evidence-based treatment. By fostering a more supportive and informed society, individuals in recovery can feel more accepted and encouraged to seek help. Reducing stigma also helps to create environments where recovery is supported and celebrated.
The Future of Addiction Treatment
The one major aspect that needs to be understood is that the field of alcohol and drug addiction treatment is not stagnant, and there are new directions and modalities that are being developed all the time for the purpose of improving the outcomes of recovery. Educational developments in the neurological field are enhancing the understanding of the brain function in addiction and thus, treatment. New approaches to treatment TMS and neurofeedback are revealed to be helpful to an extent. This is also evidenced in policies undertaken to enhance access and subsequently remove hindrances to Health Care. The outlook for the treatment of addiction remains bright as it will continue to attract scholarly research and development of more appropriate forms of recovery and treatment.
Real-Life Success Stories
Greatly motivating is when one gets to listen to other persons who have overcome all odds and regained their soberness. It is important to note that these stories illustrate the tenacity that is needed to turn around clients’ lives and incorporate such lessons and solutions into individual practice. Experience of other people identifies that one can recover hence giving hope to persons in the recovery process. Generic self-management, encouragement, and peer support may be provided to other members by the patients with long-term remission from alcohol dependence.

Resources for Mental Health and Addiction Recovery
Self-help resources are easily available for those who are in the process of the recovery session. Collective helplines, websites to Find The Best Addiction Rehab Center, and associations have data and support with suggestions for such lines. Other helpful tools include the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA), National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), and even The AA. The use of such resources can enable the users to locate the assistance they require, get treatment solutions, and meet people with similar experiences. It is possible to maximize the utilization of the resources to improve the recovery process and set the ground for sustainable abstinence.
FAQs on Mental Health and Addiction Recovery
Mental health cannot be overemphasized when it comes to the recovery of addiction. Failure to seek professional help in managing mental health issues means that the patient is bound to relapse and thus will not get well. Focusing on mental health issues as part of addiction treatment is beneficial since it assists in forming a long-term strategy for overcoming addiction as well as all associated disorders.
The disorders related to addiction are depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and PTSD. Many of these are comorbid with addiction making it paramount to treat both in order to get rid of the addiction and improve the condition.
The most efficient types of treatment are CBT, DBT, Motivational Interviewing, and Group Therapy. These therapies involve different aspects and components of mental health and addiction and work on resourcefulness and preparedness.
MAT employs the use of drugs to treat withdrawal signs as well as the desire for the substances that one is recovering from to avoid relapse. This approach to treatment entails Medication Assisted Treatment together with counseling and behavioral therapies.
Mentorship of self-help groups is an encouraging and prescribing role that contributes to the practical and sympathetic framework for carrying on long-term abstinence. Social support in terms of family and peer support groups, and community participation facilitate patient’s maintenance of positive attitude and focus hence reducing feelings of isolation and hence relapse.
Conclusion
Mental health is a critical aspect of a person who is struggling with addiction. The coexistence of mental health disorders and substance dependency makes it equally important that they both are treated as major components of the treatment program for addiction. Employing knowledge of the relationship between these aspects in the use of integrated treatment methods, human beings are to be provided with the opportunity for a happier and healthier life.